Projects
At SenticNet, we are working on several projects spanning from fundamental affective computing research to the application of sentiment analysis techniques to domains like finance, healthcare, and the arts. Each project leverages the specific expertise of one or more members of the Sentic Team but, in fact, all projects are highly interdependent and interconnected with each other. We currently have seven main projects:
• AI FOR BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE
• AI FOR CLIMATE RESILIENCE
• AI FOR EDUCATION
• AI FOR SCIENCE
• AI FOR HEALTHCARE
• AI FOR ONLINE SAFETY
• AI FOR THE ARTS
AI FOR BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE
We examine various AI adoption phases in business intelligence, tracing the evolution from the initial reliance on outsourced AI services to the integration of advanced, human-centered AI systems that enhance decision-making and operational efficiency. Our research explores how businesses transition through these phases, addressing challenges such as data governance, workforce adaptation, and the ethical implications of AI deployment. Additionally, we support managers in understanding AI from an organizational perspective, helping them grasp not only what AI is but also how it fundamentally differs from earlier waves of information technology, including group support systems and social media. By bridging this knowledge gap, we enable organizations to make informed AI adoption decisions that align with their strategic goals.
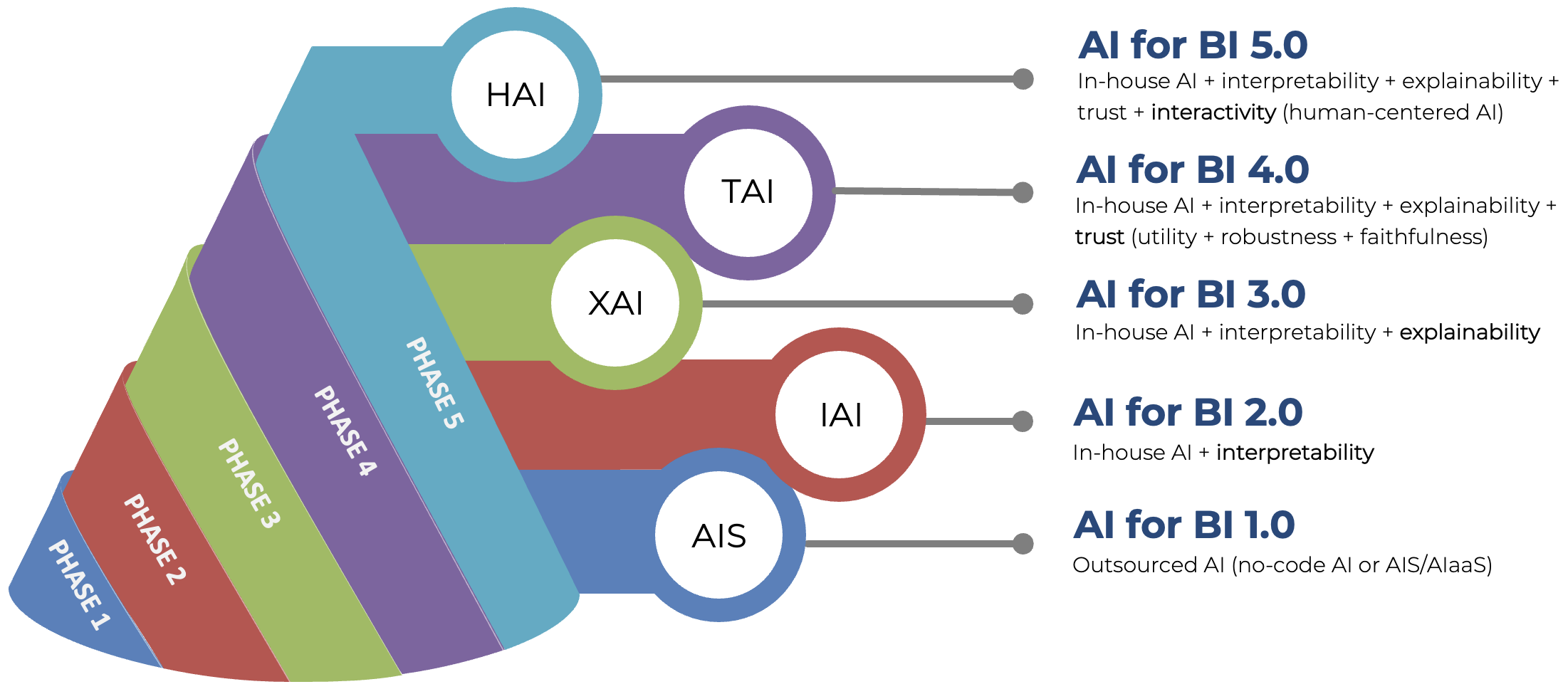
We also investigate how integrating sentiment analysis and user modeling can improve the effectiveness of recommender systems for business intelligence. By leveraging AI-driven insights, we aim to develop more accurate and personalized recommendation strategies that enhance user experience and decision-making in business contexts. Additionally, we explore the concept of responsible recommender systems, ensuring that recommendation algorithms align not only with business objectives but also with users' goals, ethical considerations, and long-term engagement. This approach helps create more transparent, fair, and user-centric models that foster trust and sustainability in AI-driven business applications.
AI FOR CLIMATE RESILIENCE
We leverage AI to deepen our understanding of and develop strategies for mitigating climate change. Specifically, we conduct sentiment analysis on climate change by collecting real-time climate-related data from diverse sources, such as ClimateTweets and ClimaEmpact. This data is then analyzed to gain insights into public sentiment and discourse, which helps us in mining public opinions about wildfires and assessing perceptions of other weather disasters. By understanding these opinions and trends, we aim to contribute to more informed decision-making and policy development in climate action.
We also harness AI to promote sustainability by developing innovative solutions tailored to environmental and corporate challenges. For example, we construct ad-hoc knowledge bases, such as ESGSenticNet, to facilitate the organization of sustainability-related information and advance explainable NLP techniques for corporate sustainability analysis, enabling more transparent and interpretable assessments of companies' sustainability practices. Finally, we leverage AI for critical applications such as greenwashing detection, helping to identify misleading environmental claims, and for deciphering public opinion of nuclear energy, providing valuable insights into societal perspectives on alternative energy sources.
AI FOR EDUCATION
AI algorithms can analyze student data and behaviors to create personalized learning pathways tailored to each student's needs, preferences, and learning styles. This individualized approach helps detect learning engagement and, hence, optimize learning outcomes. AI-powered adaptive learning platforms adjust the difficulty level and content of educational materials in real-time based on students' performance and progress. This enables students to learn at their own pace and receive targeted support when needed.

AI-driven tutoring systems enhance learning by offering students interactive, personalized instruction and real-time feedback, effectively simulating the benefits of one-on-one tutoring. These intelligent systems leverage adaptive learning techniques to adapt to students' strengths and weaknesses, ensuring a tailored educational experience. By identifying areas where students may struggle, these systems provide targeted support, reinforcing concepts and fostering deeper understanding in challenging subjects.
AI FOR SCIENCE
Scientific discovery is a key driver of progress, and LLMs have the potential to accelerate this process. However, their ability to generate novel, valid hypotheses remains uncertain. We investigate whether LLMs can autonomously propose research hypotheses based on a given background (a research question and/or survey) without domain constraints, with a particular focus on social science and chemistry. In particular, in the context of chemistry we also explore LLM limits in fine-grained scientific hypothesis discovery and experiment-guided hypothesis ranking. In general, our key research questions are: (1) Can LLMs effectively retrieve useful inspirations? (2) Can they synthesize hypotheses by integrating background information and inspirations? (3) Can they rank hypotheses based on quality and relevance?
We also apply AI in cognitive science, with a particular focus on metaphor analysis. This approach allows us to explore how metaphors shape thinking and communication across different domains. Specifically, we conduct a comparative study on metaphorical cognition in ChatGPT and humans, examining similarities and differences in how AI and human minds process figurative language. We also use metaphor analysis for unveiling diplomatic narratives, for financial metaphor analysis, for understanding the cognitive mechanisms in loan marketing, and finally for decoding metaphors in brain signals.
AI FOR HEALTHCARE
We are developing intelligent monitoring tools, e.g., Sentic PROMs and MEGACare, to be used alongside automated systems for medical code prediction and clinical predictive modeling. We also explore how sentiment analysis can extract actionable real-time information from social media for outbreak management. Additionally, we also investigate how the application of sentiment analysis in the bio-medical domain can enhance healthcare by mining unstructured medical data from text and converting it into structured machine-processable data.

We also use AI for mental healthcare, e.g., for early detection of emotion-related mental disorders, with particular focus on depression and suicidal ideation detection. Finally, we make our tools as transparent as possible by leveraging explainable AI models that enable clinicians and medical doctors to better understand and intepret the results of such tools.
AI FOR ONLINE SAFETY
AI plays a critical role in enhancing online safety across various aspects of digital interactions. One significant application lies in content moderation, where AI algorithms automatically identify and filter out harmful content like hate speech, sexism, violence, and explicit material from online platforms. Moreover, AI systems can detect instances of cyberbullying, social media shaming, and discrimination by analyzing digital content, facilitating timely intervention and support for victims.

AI algorithms also contribute to the detection of fake reviews and misinformation by analyzing news articles and online content, assisting users in distinguishing credible sources from unreliable ones. Furthermore, AI-powered systems monitor online gaming platforms for inappropriate behavior, harassment, and trolling, ensuring a safer and more enjoyable gaming experience for players.
AI FOR THE ARTS
We have several on-going collaborations with NTU ADM to promote the use of computer science for the arts but also the use of artistic devices for improving data visualization and understanding in the context of information extraction. One of such projects is about performing sentiment analysis of cultural monuments. Another project is Mood of the Planet, an installation that visualizes the emotions expressed on Twitter in real time. Social media data are collected and processed by SenticNet technologies and visualized according to the emotion-color mapping of the Hourglass of Emotions.

The results of such mapping are displayed through an interactive sculpture, a dynamic architectural installation that has as its center-piece a large ‘arch’ or ‘doorway’ that emits colored light and animates in reflection of the live emotions expressed by people around the world via Twitter. This ‘doorway’ is reflected within a wall-mirrored room where it is repeated into a tunnel-like shape, an infinity of doorways that exist as an endless cycle, or echo, of past and future in space and time, and collapsing into the eternal present. A wooden pathway traverses the room through the doorway, and connects the two mirrored walls and thus creates the ‘infinite’ pathway for the audience to walk upon.





